Printer purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
- All-in-one printers are a hotly in demand, essential piece of equipment for working from home or at the office. As well as printing, they can also scan, photocopy and fax.
- Coming equipped with inkjet, laser or LED printing technology, some models are even suitable for professional photo printing.
- Picture resolution and printing speed can be adjusted with specific built-in features, while a range of interface options make all-in-one printers accessible to a variety of user groups.
- Extras can be added to standard models to improve office efficiency or to make tasks around the home easier.
- Before purchasing, consumers should be aware of their own requirements and be able to weigh these up against the costs of ink, toner and paper.
All-In-One Printers for Use at Home
Multifunctional devices, such as all-in-one printers, really can do everything. So much so, that most offices are now unimaginable without one. More and more, all-in-one devices are also finding their way into our homes. Statistics from 2021 show that over a quarter of people in the UK are using their printer daily, while half are printing on a weekly basis. In the average year, more all-in-one devices are now sold than conventional printers. All-in-one devices come mostly in two varieties: the 3-in-1, combining a printer, a scanner and a photocopier; or the 4-in-1, which comes with fax included as well.
Printing in the Digital Age
Despite the acceleration of digitalisation and the rise of mobile technology, printers remain an essential piece of equipment. The much-promised paperless office remains a distant fantasy.
The printer manufacturing industry has reacted to the growth in mobile technology by adapting the role of the printer. Recent years have seen some of the most dynamic developments in the industry in decades. Network-compatible systems are the new industry standard, while all-in-one devices now offer enhanced connectivity. Wi-Fi, Cloud services and numerous apps make sure that printers and scanners can be accessed and used from anywhere.

From Cheap Deals to Luxury Models
The market for all-in-one printers offers something for everyone, regardless of your requirements or budget.
The price at purchase is first and foremost tied to the in-built technology of any given device. This technology is the driver of the printing speed, the resolution of printed or scanned materials, connectivity options, as well as several added features like borderless printing, double-sided scanning, or double-sided printing.
Buying a high-end model may of course not make sense for a family who rarely print, scan, or copy. In such cases, a cheaper product is likely to do everything you need with no compromises on quality necessary. Something to always be aware of when buying an all-in-one printer is the running costs for replacement ink, toner, and paper. These costs are often higher with cheaper models than with more expensive ones. Anyone interested in buying an all-in-one printer would be well advised to weigh up their own needs against the possibilities on the market.
What Types of Printer Are There?
The first thing to think about for anyone interested in buying an all-in-one printer is the print technology. A difficult choice must be made between inkjet, laser, and LED. If you wish to print out photos as well, even more factors come into play.
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers fall under the category of matrix printers. Matrix printers either shoot out or direct tiny drops of ink onto the paper to create an image. This type of printer is considered particularly low impact, as the printing process doesn’t rely on any machinery coming into contact with the material being printed on.
At home or in an office you are most likely to find a “drop on demand” (DOD) device. These work by shooting out ink drops individually.
DOD inkjet printers are categorised by the way in which ink comes out of the jets. There are two main types to choose between: the bubble-jet and the piezo. Bubble-jet printers create drops of ink which are heated until they expand. As vapour bubbles form, a drop of ink is pressed through the jet. Canon, Lexmark, and Hewlett-Packard all use this technique in their printers. Epson, meanwhile, uses the reverse piezoelectric effect in their DOD inkjet printers.
The Reverse Piezoelectric Effect
This effect describes how materials deform when an electric voltage is applied to them. Epson printers work with self-deforming ceramic components.
Inkjet printer printheads are moved on tracks by a motor-driven belt. A roller, driven by its own motor, moves the paper through the printer.
Although inkjet printers certainly have their advantages, there are other areas where they are not quite as convincing. In the table below, we’ll compare the plus points and drawbacks of buying a DOD inkjet printer.
Advantages
- Low price due to simple construction and ease of manufacture
- Almost as fast as laser printers
- High-quality printing of photos, even on coated paper
- Possible to print on other surfaces, such as on CDs or film
- Less energy consuming
Disadvantages
- Some inks are not suitable for documents or archivisation, due to susceptibility to light damage
- Best quality only possible with special paper; weak outlines with normal paper
- Black and white printing costs more expensive than with a laser printer
- Ink can dry out if not used regularly
- Too slow for large-scale printing operations
Inkjet printers are best suited for those who print regularly, but not in large quantities. For those who wish to print photos, or to print on surfaces like film, cardboard, or CD, inkjet printers come highly recommended. The main thing to take into account is the price comparison between the price at purchase and the high running costs for ink cartridges and special paper.
Laser Printer
Laser printers use exposure to light and pressure to print an entire side in one go, no matter how small the text or the images in question. This method is called electrography or, more commonly, Xerox.
The first laser printer
In 1973 in Palo Alto, California, engineer Gary Starkweather created the first laser printer for Xerox by modulating laser beams.
The central element of a laser printer is an image cylinder coated in a photoconductor. The photoconductor becomes negatively charged before a laser beam either removes the charge or weakens it step-by-step for colour gradation in the areas where the toner will later be applied. The laser beam is pointed at a rotating mirror above the image cylinder before powder is transferred by the toner onto the removed or weakened areas of the photoconductor. This carries the same charge as the image cylinder, meaning that it only sticks to the uncharged areas. The photoconductor then uses a transfer ribbon to bring the toner into contact with the paper. Newer models use printing mechanisms that have image cylinders for each individual colour, which the paper passes through one after another. On the reverse side of the paper, a strong positive electric charge causes the toner to jump onto the paper. In the last step, the paper passes through a roller heated to 180 °C, which uses pressure to stick the toner to the paper.
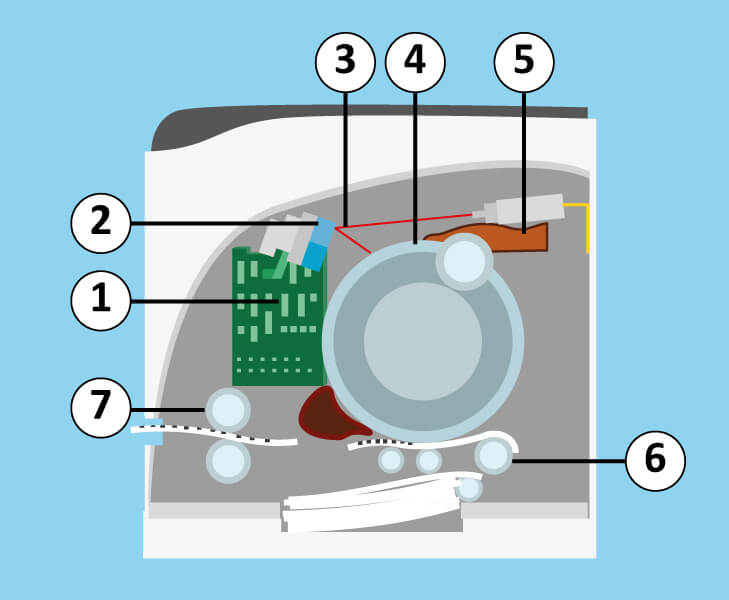
Whilst black-and-white laser printers are available for cheap, colour laser printers are usually more expensive than their inkjet counterparts. This, however, should not be the only criterion when buying a printer. It should be noted that the running costs for toner are usually much lower than those for ink cartridges. This is still the case, even when you consider the cost of regularly changing the image cylinder and other parts subject to wear and tear.
Advantages
- Bold outlines on copy and recycling paper
- Resistant to fading and moisture (UV resistant, run and wipe resistant)
- Low printing costs
- High-speed printing
- Usage on a regular basis not necessary
- Long lifespan
Disadvantages
- Comparatively large due to number of components
- Colour space and levels of contrast for photo printing often not as good as with inkjet printers
- More expensive
- More energy intensive
- Screening can remain visible
- Flaking possible if the paper gets creased
- Printing cancellation not possible halfway through
- More internal storage needed
- Gives off ozone and microparticles
- No borderless printin
- Printing only possible on flexible, heat-resistant material
For office use, a laser printer is superior to an inkjet printer in a number of areas. Laser printers are able to create a clear type face on cheap, normal paper, while coping with larger scale printing volumes at higher speeds. Most laser printers have a large paper tray, while toner normally needs to be replaced much less often than ink cartridges. Even the casual home user is sometimes better off using a laser printer, seeing as neither the print head, nor the ink cartridges can dry out after a long period of inactivity.
Laser printers are, however, only capable of printing on recycled paper, copy paper, or coated laser printing paper. Photo paper and other types of coated paper are unable to stand the high temperatures and are liable to damage the printer.
Those who occasionally want to print higher-quality images, those who print less than 100 pages a week, or those who sometimes wish to print on surfaces like film or CDs are probably best off sticking with an inkjet.
LED Printers
The methodology behind LED printers was developed in the ‘90s by Casio and is similar to that of the laser printer. For this reason, LED printers often get mistaken for laser printers in everyday conversation. In contrast to conventional laser printers, however, LED printers don’t work with the help of a mirror, neither do they scan a document from the end of one line to the next. Rather, individual lines of the original document are captured by a light-emitting diode before being transferred to the photoconductor all together. Known as a “single-pass system”, LED printers also don’t transfer colours individually onto the paper, rather all together in one step.
Advantages
- Single-pass system makes LED faster than inkjet and laser printing as templates are copied across quicker
- More compact to assemble than laser printer
- No movable parts, improved stability
- Sharper printing towards the margins
Disadvantages
- Colour space and gradation not as good as with inkjet printers
- More expensive than inkjet printers
- Printing capacity above what is needed for home use
- More energy intensive
- Flaking is possible if the paper gets creased
- Printing can’t be cancelled halfway through
- More internal storage needed
- Gives off ozone and microparticles
- Printing only possible on flexible, heat-resistant material
More and more devices are being fitted with LED printing technology. This is mostly the case with models used in medium to large-scale offices, which have to cope with high printing volumes at speed. Everyday use while working from home wouldn’t come close to pushing a LED printer to its capacity.
Photo Printers
There is no single, unified definition of what a photo printer is. Regardless of the printing technology involved, any printer that prints good quality photos could technically be classified as a photo printer. The possibility to print in high resolution and without borders is considered the main criterion. This is offered by high-resolution inkjet printers, as well as by thermal sublimation printers, more simply “thermal printers”, which work by evaporating coloured wax.

The “selfie generation”, together with widespread smartphone use, have contributed to a growth in popularity for mobile compact printers since their invention in 2008. These printers use inkless “zink print technology”. “Zink”, in this instance, has nothing to do with the chemical element, rather it’s an abbreviation for “zero ink”. Although Zink printers don’t require ink cartridges, they do require the purchase of special photo paper. This paper contains colour pigment which begins to develop upon exposure to heat. Mobile printers are rarely bigger than a smartphone and are great for instantly printing your polaroid-style snaps when out and about. It is worth bearing in mind that the image resolution is not particularly high, while there are only a few different formats available. Running costs are also high due to the need for specialised paper.
The Selphy Series from Canon is an example of a compact, Wi-Fi-compatible inkjet photo printer. These printers are specially set up for printing photos. They can be used and maintained without needing a computer, and provide tools for image editing and optimisation. For this, they require special ink and photo paper.
Conventional inkjet printers can also be set up for printing photos. This is done by allowing for borderless printing on different formats of photo paper without ink build-up at the image edges. These kinds of printers are especially well known for their high resolution.
The plus points and drawbacks of photo printers are listed in the following table:
Advantages
- Highest print quality
- Borderless printing
- High resolution
- Compact
- No need computer connection necessary
Disadvantages
- Sometimes limited to printing photos
- Need for expensive special paper
- Particularly expensive Ink and extra ink resupplies
- High ink usage
- Special functions which are unnecessary for office use
- Slow printing speed
Photo printers or inkjet printers made specially for printing photos are, in reality, only aimed at a consumer base of hobby photographers who want to use their printers first and foremost for printing high-resolution photos. For printing documents, they are often too slow and ink intensive. Inkjet technology capable of delivering high quality photos can also be built into all-in-one devices. As part of our comparison, the Canon Pixma MX925, the Brother MFC-J4620DW and the HP OfficeJet Pro 8720 all offer the possibility of borderless printing in good resolution. Canon’s printer is optimised for photo printing thanks to its multiple interfaces, SD-card slot, options for image processing and fifth ink cartridge, especially for black ink. This allows the printing of photos that are every bit as good as chemically exposed prints in terms of resolution detail and colour depth. This is how newer models are able to achieve shiny, true-to-life colours printed on specially coated paper. All-in-one devices can combine the functionality of both a photo printer and a home office printer.
All-In-One Devices
All-in-one devices come in 3-in-1 varieties, which can print, scan and copy, as well as 4-in-1 varietes, which can also fax. You can also choose between a black-and-white or colour device. Black-and-white varieties can be bought very cheaply, although they are not suitable for printing photos. For our comparison we will only look at 4-in-1 colour devices. These devices offer us the best method to evaluate based on specification, function and value for money. For those who can do without fax, pretty much every 4-in-1 model comes in a 3-in-1 equivalent from the same manufacturer.

There is no way around making the decision between inkjet, laser, and LED, when making your decision to buy an all-in-one device.
The price of an all-in-one device is generally significantly lower than the cost of buying all of the individual devices separately. In addition, all-in-one devices are a lot more compact and space economical than having multiple clumsy bits of equipment. That said, the scanning quality is not quite up to the standard of designated scanners, especially with regards to the depth of focus. For use at home or for everyday office tasks, however, all-in-one devices and the attached scanners are usually completely serviceable. The quality of the in-built printers is on a par with those of dedicated devices.
Copying, printing, and scanning with all-in-one devices is all possible via app, Cloud service, media storage interface, or control display, all without the need to even turn on a computer.
Advantages
- Cheaper than buying three or four individual devices
- Space saving
- No computer connection necessary
- Copy function
- Single control for multiple functions
- Only one power outlet necessary
- Lower energy consumption than individual devices
- Configuration from one single device
Disadvantages
- Bigger than stand-alone printer
- Scanner often not up to the standard of dedicated equipment
- Entire device influenced by malfunction or damage, instead of just one component
All-in-one devices can be bought cheaply and are a compact, multi-use tool for all occasions, be it at home or in the office. Printing and scanning are just two of the many features they offer to help with all manner of home office tasks. All-in-one devices are particularly suited to those who know exactly what features they need and how much they plan to print. The associated running costs for toner and paper are the same as those for separate devices and therefore need to be considered before buying. Because of this, multifunctional devices with laser printers are particularly suited to those who print at high volume. Models with an inkjet printer, on the other hand, are better suited for those who print comparatively less, but also wish to print photos occasionally.
Buying Criteria
The market is filled with an abundance of all-in-one printers offering different technology and parts. As a result, there is a large difference in the pricing between models. Any rash decision to buy the cheapest deal should be avoided. For anyone interested in buying an all-in-one printer, it is essential to think through your own requirements in detail. This will help you be able to compare which all-in-one device is going to best meet your expectations.
Printing and Scanning Resolution
Resolution is measured in dpi, which stands for “dots per inch”, or pixels per inch (2.54 cm). These dimensions give us a clue about the quality of a printer.
For those looking solely to print text documents, print resolution can all but be ignored. A resolution of 600 x 600 dpi is completely satisfactory for good-quality printing with a laser printer. 1,200 x 1,200 dpi is only necessary for extremely detailed images or coloured graphics.

High resolution is particularly important for users looking to print out photos. The resolution achieved by inkjet printers is generally much higher than that achieved by laser printers. A note of caution is suggested with extremely high resolution. Values like 9,600 x 2,400 dpi or 57,60 x 1,440 dpi are interpolated and calculated by the computer and therefore may not correspond to the actual final prints. The more relevant value is that of the printed resolution, although manufacturers rarely provide this information. For the reproduction of expensive art prints, for example, 2,400 x 2,400 dpi is completely sufficient, so long as quality ink and suitable paper are also used.
The resolution isn’t the only thing which accounts for the quality of a print: the choice of paper and quality of ink also play an important role, especially with inkjet printers. If the ink runs too thickly, or ink drops begin to run into one another, then fine outlines can become unclear and blended.
The same applies to scanners. Those looking to digitalise their photos should pay attention to scan quality. Alternatively, those looking to digitalise and archive everyday documentation and bills can confidently put their faith in scanners with lower resolution.
Printing and Scanning Speed
Printing and scanning speeds are usually given in pages per minute.
Higher printing speeds are clearly reflected in the cost of a printer. It’s therefore important to weigh up whether or not you need a device capable of handling large printing tasks one after another.
Due to the technology they use, laser printers tend to have higher printing speeds than inkjet printers. Most of the time, they can print in colour equally, or at least almost equally, as fast as in black-and-white. Only LED printers are quicker when comparing speeds. The top dog in our comparison for printing speeds is the OKI MC363dn, which can print 30 black-and-white, and 26 coloured pages per minute.
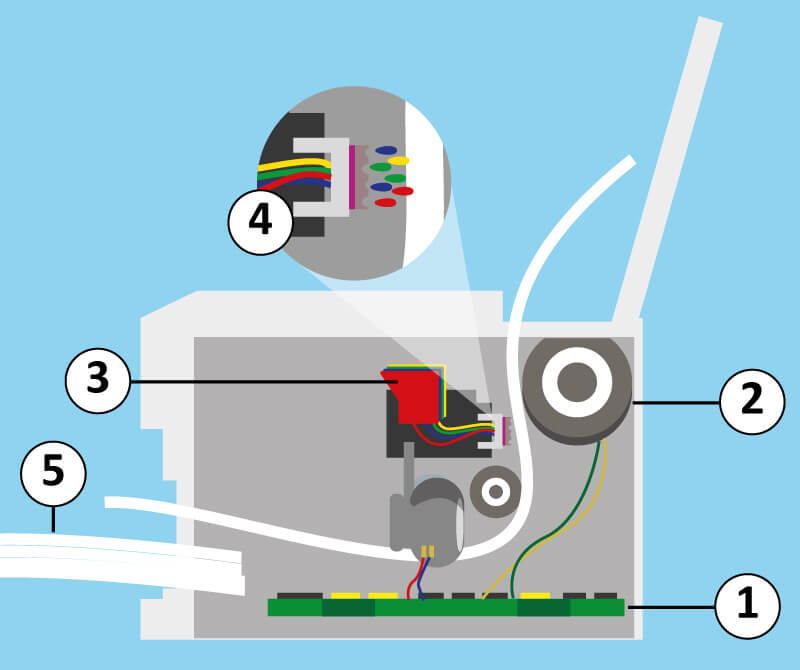
The number of jets plays an important role for the speed of printing with an inkjet printer. The general rule states that the more jets the printer has, then the quicker it can print. The order of the jets is also important as this controls how quickly the printing head moves over the paper. The numbers manufacturers provide about inkjet printing speeds are often unrealistically high and depend strongly on the quality level set during the printing process. Inkjet printers usually need a lot longer for colour printing than for simple black and white. Longer printing time for inkjet printers comes with an increase in printing quality. Information for laser printer printing speeds is, in contrast, usually correct.
Inkjet printer technology has developed to the point where they now work much faster. The printing speeds are reflected directly in the price. The most expensive model in our comparison, the HP OfficeJet Pro 8720, is capable of 24 black-and-white and 20 coloured pages per minute. The cheapest, the Epson Workforce WF-2630WF, clocks in with nine black-and-white and 4,7 colour pages – only a fraction of the speed of the HP. It’s clear that money saving comes with sacrifices in printing speed.
The same applies to the scanning unit. Here too, slowing down comes with savings. Those who rarely print and scan can make considerable savings in this area. Meanwhile, those for whom printing speeds remain important should look towards an all-in-one device with a laser printer or an expensive inkjet model.
Printing Volume
Together with printing speed, those who print at high volumes should pay less attention to the price at purchase, and more attention to the running costs for paper, ink, and toner. Looked at in this way, inkjet printers are usually a lot more expensive than laser ones. Toner cartridges for LED and laser printers generally last a lot longer than those for inkjet printers. High levels of printing quickly put the relatively low price at purchase for all-in-one inkjet printers into perspective.
| Printer Model | Printer Type | Price per b/w Page | Price per Colour Page |
| Brother MFC-J4620DW | Inkjet Printer | 2.6 p | 5 p |
| Kyocera Ecosys M5526cdw | Colour Laser Printer | 1.3 p | 8 p |
| OKI MC363dn | LED Printer | 1.7 p | 12 p |
With inkjet printers, the risk is always there that while printing at low volumes, the printhead and ink cartridges can dry out. Printhead cleaning after long periods of non-use also wastefully uses up ink.
Using an inkjet printer for larger printing tasks which entail several hundred pages of printing can often lead to frustration. This is because cartridges generally have a much lower coverage than toner and, as a result, need to be changed more often. Those using an inkjet printer for large printing volumes should consider whether XL or XXL cartridges are available for the model in question.
Printer Interface
All-in-one printers offer an abundance of different interfaces for wireless connection. Interested parties should be aware of the most important and most commonly integrated features in order to separate important features from less important ones.
Wi-Fi

All of the printers in our comparison come equipped with Wi-Fi. Network interfaces now also come as standard with all-in-one printers. As long as the device is connected with Wi-Fi to a DSL router, all of the devices connected to that network have access. This is useful when several computers in a house or an office need to connect to the printer, but the printer isn’t positioned close to the working space, or is in another room. Even if the printer is positioned right next to a computer, there is no need to connect the two with a cable as long as the device is Wi-Fi enabled.
Wi-Fi Direct

Modern multifunctional printers are usually also equipped with Wi-Fi Direct. This means that the printer can connect through direct channels. Instead of through a cable, data is transferred from a computer, smartphone, or digital camera directly to the printer. This differs from conventional Wi-Fi in that neither an internet access point nor a router is required to transfer data– the Wi-Fi compatible device provides this itself. Wi-Fi Direct compatible devices offer the advantage that documents can be printed directly from a smartphone or tablet without having to turn on a computer or laptop. This can be controlled by apps from the individual manufacturers. For this, the printer needs to support specific features. An example would be AirPrint for Apple products.
USB
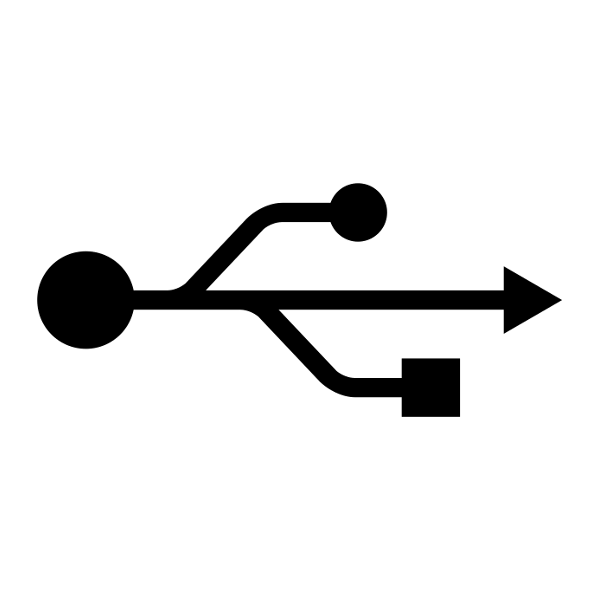
Details about USB interfaces are often not specifically addressed in all-in-one device user instruction booklets. When a device says that it is “USB 2.0 compatible”, this doesn’t confirm whether the port in question is full speed or high speed. This, however, is usually insignificant for USB connections between printer and computer, given that the printing speed is set by the ink and toner capacity of the printer and not by the speed of data transfer. Some printers offer the possibility to print or fax directly from a USB stick without having to use a computer. For this, devices must have a separate USB stick or external hard drive connection. Should this feature be available, then it will be listed by the manufacturer. The same goes for SD card slots, which allow you to instantly print your photos.
Bluetooth

Bluetooth uses a radio signal and is becoming more and more popular. Loudspeakers, electric toothbrushes, and now certain all-in-one printers come equipped with a Bluetooth interface. If the user is within a certain distance of the printer, they can send documents from their laptop, smartphone, or tablet and have them printed this way. Those who often print from their smartphone can benefit from this technique, as phone battery can be preserved by using Bluetooth.
NFC (Near Field Communication)

Most commonly, this form of wireless communication, which makes use of electromagnetic induction, is used by laser printers. This method is usually seen in contactless payment, where small sums of money are transferred through a chip. Near Field Communication is often used by businesses who have multiple, different devices working at once, as a security password can be put in place. This feature is generally not considered useful for private use.
Google Cloud Print

Devices which are compatible with Google Cloud Print allow you to print without needing to be in the same network. This means that documents can be printed off at home using Google Cloud, even if you’re out and about. To do this, follow these steps:
- Connect the printer to a network
- Connect the network to the internet
- Create a Google account
- Use Google Chrome as your internet browser
- Install Google Cloud Drive (for free)
- In the Chrome browser settings, go to advanced settings and click on the “Google Cloud Print” option under the “Manage” button and add the printer.
This should ensure that the printer is available online in your Google account. With this, you can print over Google Chrome through your mobile device.
AirPrint

AirPrint is a software interface that allows for wireless communication between a printer and an iOS/macOS device supported by a Wi-Fi network. Users of Apple products should look out for AirPrint compatibility when buying a new printer
Mopria

Android smartphone users who frequently wish to print with a variety of printers from different manufacturers may find good use for the Mopria app. Mopria is the alternative to Apple’s AirPrint. In comparison to the apps provided by individual manufacturers, Mopria offers fewer programmable options. An example would be the choice of paper. Mopria is not set up for scanning, but it can print smoothly with printers from any manufacturer.
Apps Made by the Manufacturer Each manufacturer of the products in question offers their own app, supporting devices compatible with their own products. These manufacturer-created apps are the most immediate way to wirelessly connect all-in-one printers with smartphones or tablets. They control the size and quality of the paper in use, as well as a range of other printing and scanning specifications.

Extras and Special Features
Technical specification, quality, and speed are only half of what makes an all-in-one printer. The rest is made up by extras, added features, and gimmicks. When something is missing in a particular model, the chances are that a better alternative is not far away. The following features do not come as standard but can be of interest nonetheless.
Borderless Printing
Those who often print photos or graphics in large amounts and are tired of manually removing the border should choose an all-in-one printer that supports borderless printing. Inkjet printers are best equipped technically to deal with this type of printing. Borderless printing is usually only possible in certain formats which are explicitly stated by the manufacturer. These are commonly photo formats like 10 x 15 cm or 9 x 13 cm. Printing photos on A4 is usually only possible with certain models and requires a degree of preconfiguration. When a printer is capable of printing in A4 as a standard printing option, this information will be listed in the manufacturer details.
Double-Sided Printing and Scanning
The term “double-sided printing” refers to the possibility offered by certain all-in-one printers to automatically print on both sides of a piece of paper without the need to manually remove and replace the paper. This feature can save time as well as paper. It especially pays to invest in this feature when printing in high volumes. Most of the all-in-one devices in our comparison have this feature, regardless of the printing technology they use.
Automatic double-sided scan works a little bit differently. This is only available with high-end models and is mostly supported by laser and LED devices. An automatic document feeder is a prerequisite before documents can be scanned on both sides. Only devices which offer double-sided scanning are able to offer automatic double-sided photocopying as well.
Colour Display and Touchscreen
Even in the world of all-in-one printers, touchscreens are on an unstoppable march forward. We have not, however, reached the point where every model has one yet. Touchscreens make it easier and more intuitive to use the printer control panel than it is to navigate around with buttons.
All the settings and control options (including those regarding printer software or smartphone apps for printing, scanning, photocopying, and faxing) can be controlled directly on the app without the need for an external computer, laptop, or smartphone. This allows you to print quickly and uncomplicatedly from a USB stick, SD card, or the Cloud, as well as edit, print from template, fax, or upload to the Cloud.
Automatic Document Feeder (ADF)
An automatic document feeder (ADF) is an extremely useful feature. Depending on the model, the document feeder can be filled with paper, which is then automatically loaded piece by piece. They are then passed over the scanner before coming out the other side. This is a prerequisite for double-sided scanning. That a printer has ADF doesn’t mean, however, that it can necessarily scan double-sided. For users looking to do a lot of scanning and copying, this feature is truly godsend, as the scanner works unprompted so that you don’t have to feed in every single sheet by hand.

Printing in A3
The option to print documents in A3 is a truly special feature which most of the more common all-in-one printers rarely offer. This is largely due to the fact that not many people need to print in A3 size– neither at home, nor at the office. The technology which enables printing on a device as small in construction as an A4 printer has only been available for a short amount of time. Those looking for this feature should focus directly on models which offer it. In our comparison, only the Brother MFC-J4620DW inkjet all-in-one printer supports this format. Other special models which are able to print at A3 size generally don’t offer an integrated fax feature.
Single-Ink Cartridges
When buying a printer, it’s important to pay attention to whether it comes with single, replaceable cartridges or with a multi-ink cartridge.
Those looking to buy are recommended to check the manufacturer information regarding ink cartridges. If the colour cartridge is given a single product code, then it is a multi-ink cartridge. This type of cartridge has to be completely replaced every time it runs out of one particular colour. This entails significantly higher costs as you are throwing money away every time you throw out an old cartridge. For this reason, those looking to buy should opt for a model with four to five separate ink cartridges.

Printing Cartridges
Running costs for replacing ink cartridges should already be taken into account when deciding on which model to buy. The costs start to add up when you regularly need to change colour cartridges and toner. Manufacturers recommend using their own brand of products, but this is of course the most expensive option available. Using refilled cartridges and toner from other manufacturers shouldn’t have any effect on the manufacturer’s warranty.

Manufacturer Own-Brand Ink and Toner
Every manufacturer offers corresponding ink cartridges and toner for their own models of printers. Manufacturers’ own brand cartridges provide a good finish and ideal coverage, together with high-grade colour rendering and deep shading. They are guaranteed to be compatible with the printer model in question and are easy to install. Own brand cartridges and toner are, on the other hand, the most expensive options available. Prices and coverage differ depending on the manufacturer. XL or even XXL cartridges, sometimes capable of achieving the same coverage as several toners, are available for pretty much all models of inkjet printer.

Refill Cartridges and Toner
So-called refill cartridges use the cartridge case of the original manufacturer. Another service provider then refills the cartridge by resetting the cartridge chip so that it can be recognised again by the printer. If you can tolerate a slight loss in quality, then refill cartridges are a cheaper and more environmentally friendly alternative to own-brand cartridges.
Users also have the option to refill their own cartridges. There are different methods available depending on the model of printer. Our guide shows you how it works.
Compatible Cartridges
Those looking to save money can also look to other sources for cartridges and toner. These can be produced by a completely different manufacturer. The important thing to make sure of here is that the cartridges are compatible with the model of printer in question. In terms of quality and yield, they are usually just as good as manufacturer own-brand products. Although they are often slightly more wasteful, they often come with slightly more ink as well. When compared to own-brand ink, coloured prints are sometimes a little less intense.




























 5,299 reviews
5,299 reviews




