AV receiver purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
The most important facts in brief
AV receivers provide an interface for several audio and video devices in the home cinema.
Room sound is available in different versions: from 5.1 to 13.1.
In order to be able to position the speakers well, many receivers come with their own calibration programme.
For HDR standards, the TV set and receiver must match.
AV receivers: The control centre of the home cinema
AV receivers are multi-channel amplifiers that can receive and process both audio and video data. A radio tuner is also built in. They are therefore suitable for connecting video devices such as VHS recorders, DVD and Blu-Ray players on the one hand and audio players such as CD players and record players on the other. They differ from conventional hi-fi amplifiers by the connections for video devices and the higher number of channels. While hi-fi amplifiers are primarily designed for stereo speaker pairs, AV receivers are equally suitable for multi-channel systems such as Dolby 5.1 or 7.1.
They are particularly practical because they combine the capabilities of several devices without taking up much space. In terms of width, they correspond to the usual dimensions of hi-fi equipment. The user can choose the source of the signal that the connected speakers output. This also applies to the video source, as AV receivers have a choice of video outputs. So, in a way, they are the control centre of many home cinema systems.

A classic FM radio tuner is on board by default, because its installation hardly confronts the manufacturers with higher production costs. Since December 2020, all AV receivers have also been equipped with a DAB+ tuner for receiving digital radio programmes. In addition, the option to receive internet radio is integrated in many devices.
What matters when buying
Since AV receivers must be able to receive and, if necessary, convert a wide variety of audio and video formats, there are many criteria that distinguish the devices from one another.
Weight and size
In order to present a coherent picture in the hi-fi rack, the width and depth of the AV receivers correspond to the dimensions of CD players and cassette decks. Only the height of most models exceeds this, which is due to the larger connection panel on the back. The weight, on the other hand, is of little importance, since in most cases the amplifiers remain in the same place and are rarely moved.
Power and impedance
A much more important distinguishing feature is the power of the amplifier unit per channel. The amplifier provides a certain amount of power, which the speakers consume. In addition to the output power in watts, manufacturers often also specify Watt-RMS for the power. For loudspeakers, the wattage always stands for the power handling capacity. When buying, the user should make sure that the values of the speakers and the AV receiver match.
In this context, the impedance, given in ohms, also plays a role. If the speakers have a higher impedance than specified at the outputs of the AV receiver, their performance will drop accordingly. Compatible speakers for home cinema use, however, are usually designed for the common values.
Multi-channel standards
AV receivers are capable of reproducing various surround sound audio formats, depending on the integrated decoder. The most common formats are 5.1 and 5.2, respectively, and 7.1 and 7.2. The first digit indicates how many speakers play the sound from different directions to create the surround sound. The 1 or 2 refers to the number of subwoofers responsible for low-frequency reproduction. The system takes advantage of the fact that low tones cannot be located so precisely.

Interfaces
To be prepared for as many audio and video devices as possible, AV receivers have a variety of interfaces: from HDMI and ARC to USB and Bluetooth.
From HDMI to SCART
Particularly important is the HDMI connection, a digital port that transports picture and sound simultaneously. For example, CD, DVD and Blu-Ray players, game consoles and beamers can be connected to the HDMI input. The HDMI output of the receiver can in turn be connected to the TV or monitor.
The component video connection transmits the picture signal via three separate cinch cables. Very high-quality devices use BNC sockets. This technology is actually considered obsolete since the spread of digital connections. The S-video connection is also analogue, but its transmission quality is not quite as good. This is found on many older computers and is usually a 4-pin DIN socket.
Composite video is a single-channel image transmission method whose transmission quality is still below that of S-video. In Europe, the SCART connection has become established for this purpose – but even this is now considered obsolete. Older devices such as VHS recorders or older game consoles can still be connected via this interface. Of the video inputs mentioned, however, the HDMI variants are always to be preferred because they offer the best picture and sound transmission quality.
ARC and AUX
The HDMI port marked with “ARC” is a special feature. The abbreviation stands for “Audio Return Channel”. This is where the AV receiver receives the sound signal from the TV.
This is useful when a programme is called up directly on the TV, for example through the pre-installed app of a streaming service. Then the sound of the programme is played from the system connected to the receiver without the user having to lay a separate audio cable. The HDMI connection is identical to the one on which the TV receives the picture material, which runs from other sources via the receiver.
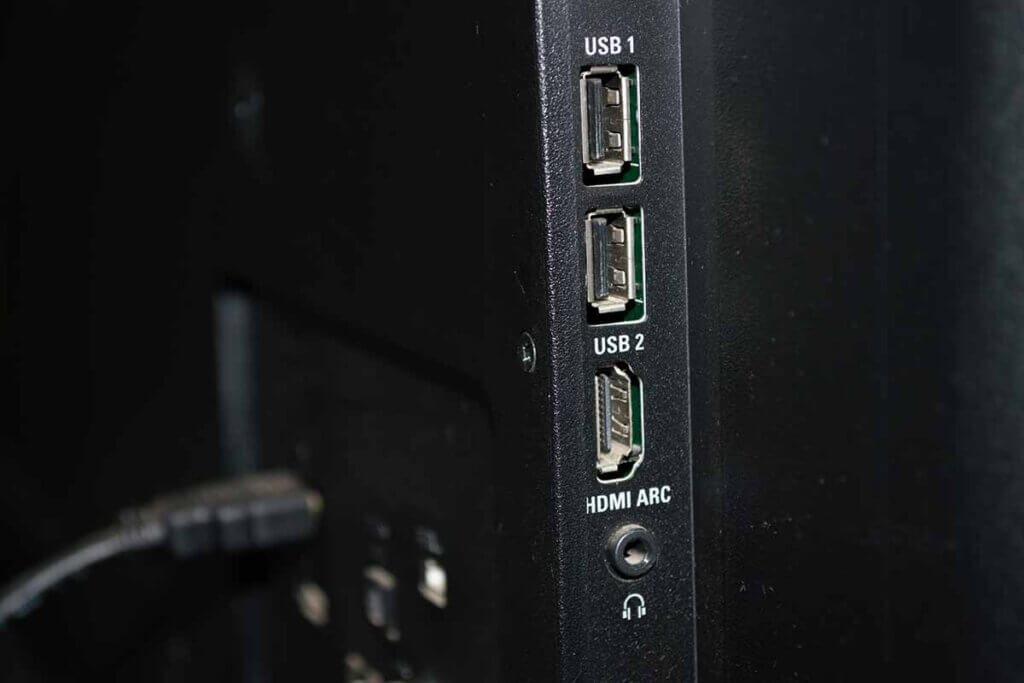

AUX outputs in the form of stereo RCA plugs are suitable for sending audio signals by cable to other peripheral devices such as audio recorders or active speakers.
USB, (W)LAN and Bluetooth
USB ports are handy for reading content from a USB stick or an external hard drive. A LAN connection establishes the connection to the home network. This way, the user can access his media server via the receiver and retrieve the content stored there, if the multi-channel receiver is equipped with this function. This is also possible via WLAN, but the wireless connection is often more susceptible to interference. Bluetooth is also a way to establish a wireless connection between the playback device and the AV receiver. This can be a PC, laptop or smartphone.
Supported formats
Common audio formats supported by AV receivers are MP3, FLAC and DSD. While MP3 files have a strong data reduction, FLAC files are considerably larger in comparison. On the other hand, they have a better and, in contrast to MP3, even lossless sound quality. Here, everyone must decide for themselves how much value they place on support for these formats. If you don’t want to listen to FLAC files with your AV receiver anyway, you can do without this support. The same applies to DSD. It is mainly used for Super Audio CDs. However, the sonic advantages of this technology are disputed among experts.
The situation is somewhat more complicated with the sound formats in which the films are encoded. In home cinema, the three most common systems are Dolby, DTS and Auro. The respective names also directly indicate the company that developed the technology.
Dolby
Dolby Surround encodes sound effects in the stereo signal in such a way that a room sound is created with a compatible receiver. The user can use one or two surround channels, i.e. either two or four speakers. A centre channel is formed from the equal parts of the front signals. Although there is no separate subwoofer channel, this is simply created by filtering the low frequencies. With Dolby Digital, there are up to five discrete channels for surround sound and a designated subwoofer channel (5.1). Those who do not have this number of speakers can configure the receiver to output the signal through other configurations such as 2.0 or 2.1. Dolby TrueHD is an uncompressed further development of Dolby Digital, with which up to 7.1 channels are possible.
DTS
DTS was developed in parallel with Dolby, so to speak, and compresses the data to a lesser extent. Here, there is also the 5.1 format and the possibility to down-convert this to 2.0 depending on personal circumstances. DTS-HD Master Audio is a lossless encoding that can also reproduce up to 7.1 channels.
Auro 3-D
This method is somewhat more complex in terms of speaker placement, because it works with three levels instead of two, as Dolby or DTS do. Each channel is already mixed into the sound track. This solution allows channels from 9.1 to 13.1. Characteristic of the format is the loudspeaker placed above the listening position with the “Voice-of-God” channel.
Video upscaling
In addition to these audio decoding techniques, some AV receivers have the ability to upscale the video input signal for high-resolution screens. This is commonly referred to as video upscaling or video upsampling.
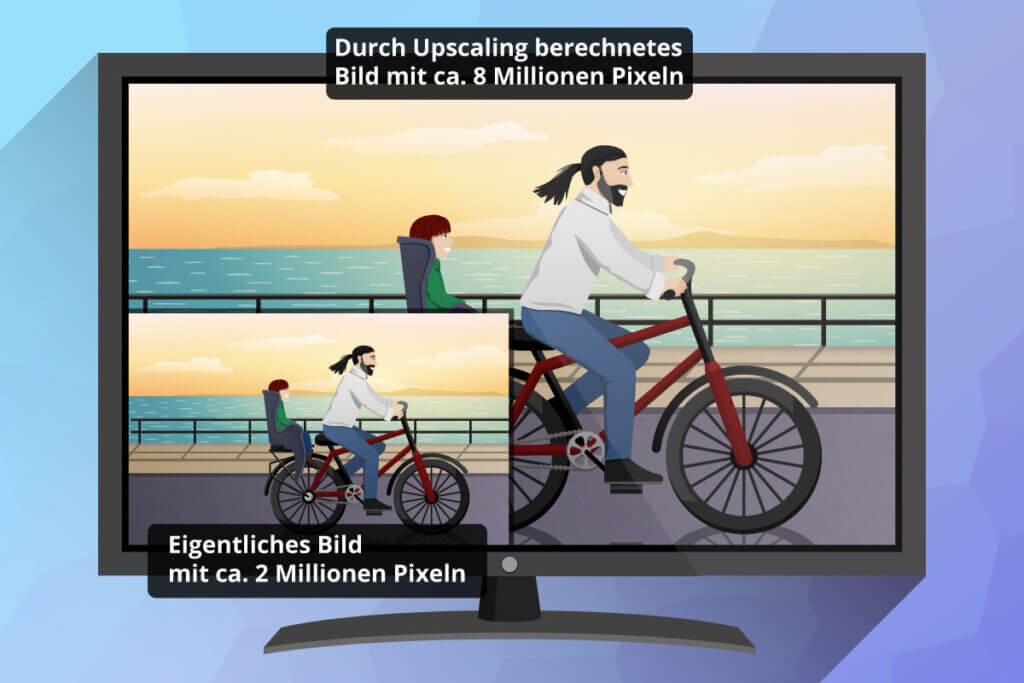
The function of the scaler is to convert the existing video signal into another resolution. Thus, the DVD resolution with 576 lines can be up-converted to Full HD with 1,080 lines, so that a cleaner picture without visible pixels is produced on a Full HD TV. However, nowadays many TVs are also equipped with this technology. If in doubt, simply test which upscaling unit, whether in the receiver or TV, produces the better picture.
But no matter which variant you choose: Upscaling can never convert a low-resolution video signal into true HD or UHD. The signal is merely upscaled to a higher resolution. It is true that a good scaler can produce respectable results. But to make full use of HD formats, all playback and recording devices must support HD technology.
TVs, monitors and beamers can only show images in one resolution at a time. Therefore, it is important to adapt signals in other resolutions by using the upscaling function of the receiver. To achieve this, the device calculates missing picture information in the original and inserts it where it should actually be in the original. This expansion by new pixels, which takes place in real time, is also called interpolation by some manufacturers.
Which HDR standards are important?
The abbreviation HDR stands for “High Dynamic Range”. This technology has nothing to do with pure image resolution, but enables a higher contrast range. At IFA 2017, two competing techniques were presented, namely Dolby Vision and HDR10+. It is important that AV receivers and TVs support the same technology. This is usually the case when both devices come from the same manufacturer. For example, Samsung often does not support Dolby Vision, while some receivers or TVs from LG do not support HDR10+.
Can I connect boxes via radio?
The multitude of satellite boxes that a 5.1 or even 7.1 system requires makes not only the installation but also the cabling a real challenge. Manufacturers have recognised this and developed systems in which the AV receiver transmits the sound completely via radio to the speakers and subwoofer. If this function is not integrated into the AV receiver, there is also the option of retrofitting it with a special wireless kit. They are offered by several manufacturers. The transmitter module is then simply connected to the corresponding audio outputs and the receiver module is connected to the subwoofer or the active speakers.
Well-known brands
Yamaha | Marantz | Denon | Teufel | Sony
The correct positioning of the surround system
For the surround sound to develop its full effect, the correct positioning of the speakers is elementary. As far as the operation of the connection panel is concerned, there are good tips on the Internet.
In order to measure the complete system, i.e. to send to each speaker the optimal sound for its position, many units have a corresponding programme integrated. In these cases, a measuring microphone is included in the scope of delivery. The user achieves an optimal result if he can place it on a stand at the viewer’s position, where it does not wobble and no sound reflections, for example from chair backs, can occur. In addition, a distance meter using laser technology is helpful to precisely check the distance to the speakers.
After the test run, the programme displays the measured distances from the viewer’s position to the respective speakers. The user can now check these with the help of the distance meter and correct them in the menu if necessary. This procedure ensures that the system reacts as well as possible to the special sound characteristics of the room and thus provides a realistic room sound.
















 646 reviews
646 reviews




